A Guide to PP Acid and Alkali Cabinet Ventilation Configuration: Does the Ventilation System Need to Be External?
When it comes to storing corrosive chemicals such as acids, alkalis, and solvents, proper ventilation is an essential aspect of safety. Many industries, including laboratories, research centers, chemical plants, and pharmaceutical facilities, rely on PP acid and alkali cabinets to safely store these hazardous materials. However, it’s not just the chemical resistance of the cabinet that ensures safety — the ventilation system plays a critical role in maintaining a safe environment for workers and preventing dangerous chemical reactions.
A common question that arises when setting up chemical storage is: Does the ventilation system need to be external? In this blog post, we’ll explore the importance of ventilation in PP acid and alkali cabinets, the different types of ventilation options available, and the best practices for setting up an effective and safe system.
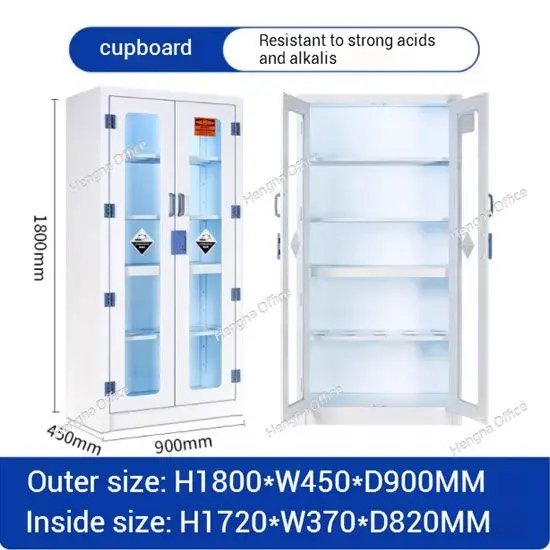
Why is Ventilation Important in PP Acid and Alkali Cabinet?
Before diving into the details of the ventilation system, let’s first understand why it’s so crucial to have proper ventilation when storing chemicals in PP acid and alkali cabinet.
- Preventing Fumes Build-Up: Many acids, alkalis, and solvents release harmful fumes, gases, or vapors that can be toxic or corrosive. If these substances are not vented properly, they can accumulate inside the cabinet and create dangerous conditions.
- Reducing the Risk of Chemical Reactions: Some chemicals can react with the air or with other chemicals when they release fumes. Ventilation ensures that these reactions are minimized by preventing the build-up of potentially explosive or toxic gases.
- Ensuring Safety of Workers: In environments where workers are exposed to volatile chemicals, proper ventilation protects them from inhaling toxic vapors. It helps to keep the air clean, reducing the chances of chemical exposure that could lead to health problems.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are required to comply with specific safety standards and regulations regarding chemical storage. Proper ventilation ensures compliance with these guidelines, minimizing the risk of fines or penalties from regulatory bodies.
External Ventilation vs. Internal Ventilation

When configuring a ventilation system for a PP acid and alkali cabinet, one of the first decisions to make is whether the system should be external or internal. Let’s examine both options and their advantages:
1. External Ventilation
External ventilation involves connecting the PP acid and alkali cabinet to an external exhaust system. This means that any harmful fumes, vapors, or gases released inside the cabinet are directed outside the building or facility. This type of system is common in larger facilities where many chemical cabinets are used, and the volume of air that needs to be filtered is substantial.
Advantages of External Ventilation:
- Effective Fume Removal: External ventilation in PP acid and alkali cabinet ensures that harmful fumes are removed from the environment entirely, reducing the risk of exposure to toxic chemicals.
- Preventing Indoor Contamination: By venting gases outside, external ventilation prevents contamination of the indoor air, which is especially important in labs or facilities with multiple people working in close proximity.
- Increased Airflow: External systems in PP acid and alkali cabinet generally provide higher airflow, which is suitable for cabinets storing large quantities of volatile chemicals.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Installation Cost: Installing an external ventilation system can be expensive due to the need for ducts, fans, and other infrastructure.
- Space Requirements: An external exhaust system requires space for venting pipes or ducts, which may not be available in all facilities.
- Complexity: The installation and maintenance of external systems are more complex compared to internal ventilation systems.
2. Internal Ventilation
Internal ventilation in PP acid and alkali cabinet, on the other hand, uses a built-in system within the cabinet to filter and recirculate air. This type of ventilation does not require an external venting system, as the air is typically filtered and cleaned before being returned to the room.
Advantages of Internal Ventilation:
- Cost-Effective: Internal ventilation systems are generally cheaper to install as they do not require complex ductwork or external piping.
- Space-Saving: Since the system is contained within the cabinet, it does not take up additional space in the facility.
- Easier Maintenance: Internal systems are often easier to maintain, as they don’t require external connections or adjustments.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Airflow: Internal ventilation systems may not provide as much airflow as external systems, which could be a limitation for storing large quantities of volatile chemicals.
- Potential for Recirculating Contaminants: If not properly maintained or if filters become clogged, an internal ventilation system could recirculate harmful chemicals back into the air.
Key Factors to Consider for PP Acid and Alkali Cabinet Ventilation

When choosing a ventilation configuration for your PP acid and alkali cabinet, there are several factors to consider to ensure optimal safety and efficiency.
1. Type of Chemicals Stored
The type of chemicals you plan to store in the cabinet significantly impacts your ventilation requirements. For example:
- Acids like sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid release fumes that are harmful to both the environment and human health.
- Alkalis like sodium hydroxide can release gases that react with moisture in the air, producing caustic conditions.
- Solvents and flammable chemicals like acetone or alcohol are highly volatile and can create dangerous fumes that pose fire risks.
For chemicals that produce a significant amount of fumes, an external ventilation system is often the safer choice. For less volatile substances, internal ventilation might suffice.
2. Size of the Cabinet
The size of the PP acid and alkali cabinet also determines the ventilation requirements. Larger cabinets, which store more chemicals, will require more airflow to effectively remove fumes and gases. Smaller cabinets may not require as much airflow, so an internal ventilation system might be sufficient.
3. Airflow and Fan Capacity
The efficiency of the ventilation system largely depends on the airflow and fan capacity. The system should be designed to ensure that the air inside the cabinet is replaced frequently enough to prevent the accumulation of hazardous gases. As a general rule, cabinets storing highly reactive chemicals should have a fan capable of moving air at a higher rate to ensure safety.
4. Local Regulations and Standards
Different regions and industries have regulations governing the safe storage and ventilation of chemicals. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) guidelines often dictate specific ventilation requirements based on the chemicals being stored. Make sure to familiarize yourself with local regulations to ensure your PP acid and alkali cabinet complies with safety standards.
5. Cost and Maintenance
External ventilation systems can be expensive to install and maintain. However, they are more effective in the long run, especially in larger facilities. On the other hand, internal ventilation systems are cheaper to set up and maintain but may not be suitable for facilities that store a large volume of hazardous chemicals.

Best Practices for PP Acid and Alkali Cabinet Ventilation
Regardless of whether you opt for external or internal ventilation, here are a few best practices to follow when setting up ventilation for your PP acid and alkali cabinet:
- Install a Proper Exhaust System: If you choose external ventilation, ensure that the exhaust system is designed to handle the volume of fumes produced by the chemicals being stored.
- Use High-Quality Filters: For internal ventilation systems, make sure that the filters are capable of trapping toxic fumes and gases. Replace filters regularly to maintain the system’s efficiency.
- Monitor Air Quality: Consider installing a monitor to measure the air quality within the cabinet and the room. This will help you track the levels of chemical vapors and ensure the ventilation system is working effectively.
- Maintain Ventilation Systems Regularly: Regardless of the system you choose, regular maintenance is key to ensuring the continued safety of the storage area. Check the airflow, clean filters, and inspect ducts for any potential blockages.
- Create a Safe Working Environment: Ensure that all personnel are trained on the importance of proper ventilation and the safe handling of chemicals. Implement emergency protocols in case of ventilation failure or chemical leaks.
Conclusion
In any facility where chemicals are stored, proper ventilation is critical to ensuring the safety of both the environment and the workers. Whether the ventilation system needs to be external or internal depends on various factors, including the type and volume of chemicals stored, the size of the cabinet, and local safety regulations. By understanding these factors and implementing the appropriate ventilation configuration, you can create a safer and more efficient storage environment for your chemicals.




